Data is any raw facts or unprocessed facts that you can record like the name of a person, name of a place, any kind of text, images, audio-video, etc. All these are called Data. When this data is processed into something meaningful then it is called Information.
What is a Database?
The database is a collection of related data. Data that is not related cannot be referred to as a database.
For example: Online banking system database or library management system database.
What is a Data Model?
A data model is a representation that displays a set of tables and the relationship between them. It gives us an idea of how the final database system will look like. There are three primary data models:
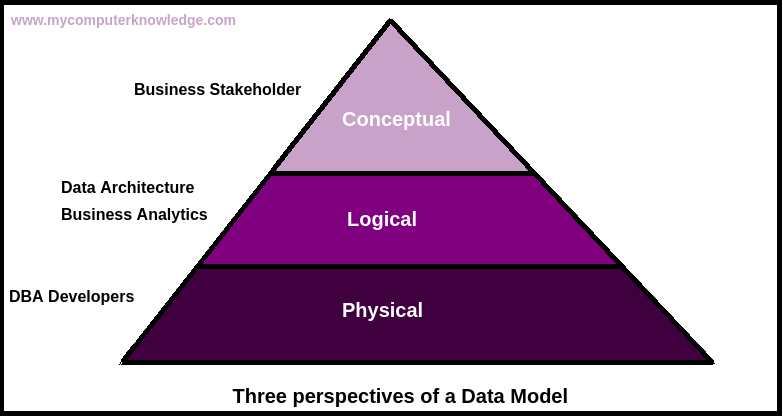
[1] Conceptual Data Model
The conceptual data model is just a set of square shapes connected by a line. The square shape represents an entity, and the line represents a relationship between the entities. A conceptual data model can be easily drawn on a piece of paper. It need not be a digital document. This makes it easy and quick to change and can be rapidly updated.
Key Points:
- Highly abstract
- Easy to understand
- Focus only on Entity
- Relationships are abstract
- No dependency on any software
[2] Logical Data Model
The logical data model is an expansion of the Conceptual data model. It forms a base for the physical model. It includes data attributes. The logical data model is used in data warehousing.
Key Points:
-
-
-
-
- Has Attributes for every entity
- More detailed than conceptual data model
- Presence of Key and Non-key attributes
-
-
-
[3] Physical Data Model
This is the most detailed data model. It gives us an abstraction of the database. In the physical model, all the components are specified. It creates a blueprint or schema. The physical model represents tables, columns, and their constraints(NULL, NOT NULL, etc.)
Key Points:
-
-
-
-
- Entity is referred to as Table
- Attribute is referred to as a column
- Includes Indexes, constraints, triggers, etc.
- Is difficult to understand
-
-
-
also see
| C Programming language |
Go Programming language |
| Linked List | Array |
| Simplification | Queue |
| DBMS | Reasoning |
| Aptitude | HTML |






































